Signs Your Hive is Thriving
Beekeeping is a fascinating blend of art and science. Grasping the health of your beehive is essential for effective management.
This guide delves into what makes a beehive truly thrive. It covers everything from the indispensable role of a healthy queen bee to the importance of a rich supply of pollen and nectar.
It also points out the key indicators of hive health and the various factors that influence it. The guide offers practical tips to ensure your bees flourish in a vibrant and productive colony.
Whether you re an experienced beekeeper or just beginning your journey, this information is crafted to help you cultivate a vibrant and productive hive. Ensuring the wellness and happiness of your bees is our priority.
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- What is a Beehive?
- How Does a Hive Thrive?
- How Can You Tell If Your Hive is Thriving?
- What are the Factors that Affect Hive Health?
- How to Ensure Your Hive is Thriving?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are some signs that my hive is thriving?
- How can I tell if my hive is healthy, strong, and showing signs of wellness?
- What does it mean if my hive has a lot of honey stores and weight?
- Do I need to see the queen bee to know if my hive is thriving?
- What if my hive has many bees but no honey stores?
- Can a hive still be thriving even if it has some dead bees outside?
Key Takeaways:
- A thriving hive is characterized by an active and healthy queen bee, consistent brood pattern, abundance of pollen and nectar, low levels of varroa mite infestation, and calm and productive bees within a well-maintained structure.
- Factors such as weather, food sources, pest and disease management, and beekeeper’s care can greatly affect hive health and productivity.
- To ensure a thriving hive, conduct regular inspections, provide adequate food sources, manage pests and diseases properly, and maintain a clean and organized hive. Educating yourself on beekeeping best practices and understanding the Warr and Langstroth methods are also important.
What is a Beehive?
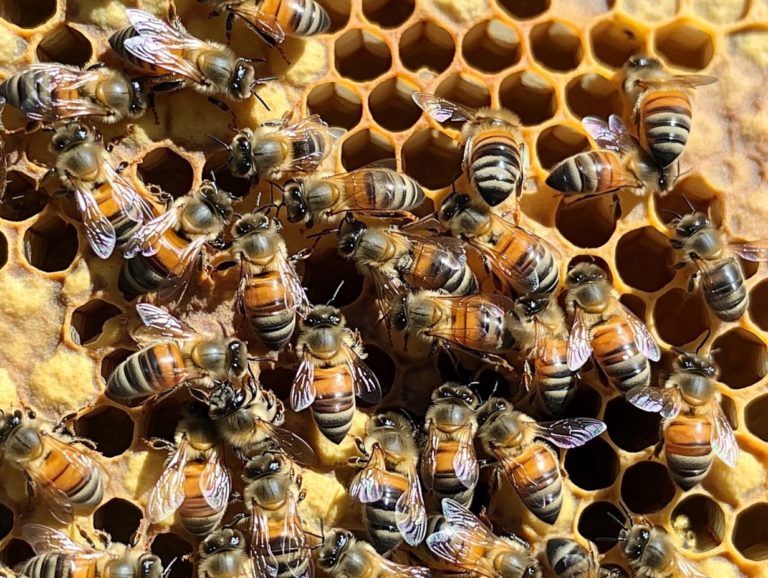
A beehive is an intricately crafted habitat that serves as a sanctuary for a colony of bees, primarily Apis mellifera.
Within this bustling community, bees thrive, produce honey, and nurture their young. Each beehive consists of a series of frames or combs made from beeswax, which the bees utilize to store honey, pollen, and brood.
The elaborate architecture of a beehive, characterized by hexagons, fosters a vibrant colony led by a queen bee. Her primary responsibility is to ensure the colony s growth and productivity.
Understanding how a beehive works can set you up for beekeeping success! By grasping the components and functions of a beehive, you can ensure the equilibrium and happiness of your bees.
How Does a Hive Thrive?
For a hive to truly thrive, it demands both your attentive care as a beekeeper and the perfect environmental conditions. Think warmth, humidity, and abundant access to natural resources like nectar and pollen.
A flourishing hive is marked by lively bee activity, impressive productivity, and a robust colony. These are all vital components for successful honey production and the overall health of the hive.
Your role as a beekeeper is pivotal in crafting these ideal conditions. This allows the bees to gather resources effectively and sustain a harmonious ecosystem within the hive.
Monitoring the hive’s weight and ensuring proper honey storage are key aspects of this role. Act now! Ensuring these conditions can prevent problems before they escalate.
How Can You Tell If Your Hive is Thriving?
Identifying the signs of a thriving hive is crucial for you as a beekeeper dedicated to nurturing a productive colony.
Key indicators to look for include an active and healthy queen bee, consistent brood patterns, and a plentiful storage of pollen and nectar within the hive. Visual cues such as the bees’ dance and vibrant colors in the hive can also signal health.
Low levels of varroa mite infestation also indicate a thriving hive. Calm, industrious bees are strong signals that your hive is indeed flourishing.
By conducting regular hive inspections and keeping an eye out for these telltale signs, you can take timely actions to safeguard the ongoing health and productivity of your colonies.
1. Active and Healthy Queen Bee
The presence and activity of a healthy queen bee are essential indicators of hive health and productivity. She is not just a figurehead; her role involves laying eggs and maintaining the colony s population and structure.
But her responsibilities extend far beyond reproduction. She secretes chemicals that help regulate behavior within the hive, creating a cohesive and well-functioning community.
As a beekeeper, it s crucial for you to be vigilant in identifying signs of a strong queen, such as the presence of brood in various developmental stages and an active laying pattern. A thriving queen will consistently produce pheromones that foster harmony among the worker bees.
On the flip side, if a queen is failing, you may notice signs of disorganization within the hive, reduced brood, and increased aggression. These red flags can indicate a potential collapse in the colony’s efficiency and strength.
Monitoring these signs emphasizes your responsibility to act and promptly address any issues that arise.
2. Consistent Brood Pattern
A consistent brood pattern is a strong indicator of a healthy hive, reflecting the queen bee’s reproductive success and the colony’s ability to sustain its population.
To assess these brood patterns effectively, you should regularly inspect the hive structure, paying close attention to the comb layout and how the brood cells are utilized. Look for any irregularities that might signal trouble. A typical healthy pattern will show a solid area of capped brood encircled by larvae in various developmental stages, which is a clear sign that the queen is actively laying eggs.
However, several factors can disrupt these ideal brood patterns. Pests like Varroa mites, diseases such as American foulbrood, and environmental stressors including fluctuating temperatures and poor foraging conditions can all pose significant threats. You must monitor these elements to help the colony grow and remain sustainable. After all, thriving brood is critical for maintaining a robust workforce and facilitating future population increases. Regular checks on your hive and knowing the signs of health can help you act quickly when needed.
3. Abundance of Pollen and Nectar
An abundance of pollen and nectar stored in the hive is a critical indicator of a thriving colony, as these resources are essential for feeding the brood and sustaining the overall health of your hive.
Pollen and nectar are crucial for young bees’ growth. They also help keep the queen and worker bees strong. By prioritizing resource availability through practices such as strategic foraging, suppressing feeding during lean times, and planting a diverse array of flowering plants, you can substantially enhance honey production.
This careful management of pollen and nectar ensures that your bees have the necessary energy to fulfill their essential roles within the hive, leading to a robust population and improved hive vitality. Optimizing resources is crucial for successful beekeeping, and you don’t want to miss it. Happy, well-fed bees can better resist diseases and pests, ensuring a thriving colony.
4. Low Levels of Varroa Mite Infestation
Keeping varroa mite levels low is key to a thriving hive. These pesky parasites can wreak havoc on the health and productivity of your bee colony, so vigilance is key.
Unchecked varroa populations can compromise the immune systems of your bees, making them more vulnerable to diseases and leading to a decline in honey production. To tackle this issue, you should regularly monitor mite levels using methods such as sticky boards or alcohol wash tests. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions when necessary, ensuring the overall health and strength of your hive.
Implementing integrated pest management strategies means using various techniques to keep pests under control. Consider these effective measures:
- Using miticides when the situation calls for it,
- Fostering a robust population of resistant bee stock,
- Employing natural remedies like essential oils.
Maintaining optimal hive conditions, ensuring your bees have proper nutrition, and encouraging hygienic behaviors are vital steps in sustaining hive health and productivity against these relentless pests. Cleanliness is key, as a well-maintained hive can help reduce the impact of varroa mites and other stressors. Act quickly! Don’t let pests ruin your hive!
5. Calm and Productive Bees
Calm and productive bees are your best indicators of a thriving hive environment, signaling that the colony is functioning smoothly and is free from major stressors.
By closely observing their behavior, you can glean valuable insights into their overall well-being. A tranquil hive typically suggests that the bees are flourishing, exploring their surroundings, and diligently engaging in vital tasks like foraging and brood care without interruptions.
Bee monitoring and paying attention to visual cues can provide significant insights into the hive’s health. As a beekeeper, when monitoring these activities, you should pay attention to specific signs such as consistent activity at the entrance, harmonious communication among workers, and a noticeable absence of aggressive behavior.
Any fluctuations in these patterns may hint at underlying issues, like disease, pests, or environmental stress. The bees’ dance and vibrant palette of colors can also be visual cues to monitor.
Maintaining vigilance in tracking bee activity not only safeguards the vitality of the hive but also enhances honey production and promotes sustainability. Regular hive inspections and understanding the environmental conditions the bees are in are crucial aspects of hive management.
6. Proper Hive Maintenance
Proper hive maintenance is essential for ensuring that all indicators of hive health are thriving, enabling the bees to flourish in their environment.
Regular inspections are not just important; they’re crucial for a vibrant bee community! They allow you to keep a close eye on pests, diseases, and the overall strength of your colony.
Employing effective management techniques, such as ensuring sufficient food supplies and best hive locations, can cultivate a vibrant community of bees. Consider the seasonal changes and implement disease control measures to ensure a thriving hive.
You should also embrace seasonal hive management, addressing the colony’s needs as temperatures shift and floral resources evolve. Understanding these best practices can significantly boost the health of your hives!
By implementing these practices, you can foster not only productive hives but also resilient ecosystems. Ensuring the bees have proper food sources during winter and maintaining the hive structure are crucial aspects.
What are the Factors that Affect Hive Health?
Factors that affect hive health include environmental conditions like warmth, humidity, and availability of natural resources. Monitoring bee behavior and ensuring a balanced ecosystem within the apiary are essential for maintaining a thriving colony.
Several factors profoundly influence hive health, and it’s essential to consider them all. Weather conditions can dictate the activity levels of your bees, while the availability of food sources directly impacts their nutrition.
Managing pests and diseases effectively is vital to protect your colony! The overall care you provide as a beekeeper is paramount. Each of these elements plays a vital role in nurturing a thriving bee colony, ultimately ensuring optimal productivity and well-being.
1. Weather and Climate
Weather and climate play a pivotal role in shaping your hive’s conditions, directly influencing bee behavior, foraging patterns, and overall hive productivity.
Fluctuations in temperature and humidity can either nurture or undermine the health of your hive. For example, extreme heat can accelerate the evaporation of stored honey, depleting the resources available to your colony, while colder temperatures may compel bees to cluster together, restricting their foraging opportunities.
Given this ever-changing environment, effective environmental monitoring becomes essential. It gives you the power to evaluate these shifts and adjust your hive management practices as needed.
By grasping how weather conditions govern hive dynamics, you can cultivate healthier colonies and boost honey production, ultimately promoting a sustainable approach to beekeeping.
2. Availability of Food Sources
The availability of nectar and pollen as food sources is essential for the health of your hive, directly impacting the bees’ ability to gather resources and sustain their colony.
Understanding the critical role of these food sources is essential. You can implement effective measures to support your bees’ foraging activities by planting a diverse array of flowering plants and establishing various blooming periods. This cultivates an environment that encourages your bees to forage more efficiently.
Effectively managing hive supplies means closely monitoring food reserves and supplementing when necessary to ensure your bees receive adequate nutrition, especially during times of scarcity. This proactive strategy not only boosts colony vitality but also enhances pollination efforts, leading to improved yields for the surrounding ecosystems.
3. Pest and Disease Management
Effective pest and disease management is critical to maintaining hive health and preventing losses in bee populations, especially from Varroa mites, a common parasite affecting bees.
To achieve this, you should adopt a blend of preventative measures and targeted treatments, customized to the specific threats your colonies face. Regular monitoring techniques, like drone and debris checks, enable early detection of issues, allowing you to intervene in a timely manner.
By implementing best practices including maintaining genetic diversity in your bee populations, ensuring proper ventilation within the hives, and employing strategies that combine different methods to manage pests effectively you will enhance the overall resilience of your hives. These holistic approaches tackle immediate pest and disease challenges while also fostering long-term health and productivity within your apiary.
4. Beekeeper’s Care and Management
The level of care and management you provide as a beekeeper is a fundamental factor that influences the overall wellness of your hive and its bees.
To grow a thriving colony, actively monitor hive conditions paying attention to temperature, humidity, and the presence of any pests or diseases. Regular inspections are essential, as they allow you to intervene promptly when issues arise. Adhering to best practices means ensuring your bees receive adequate nutrition during lean seasons and that they have enough space to flourish, which often entails adding supers as the colony expands.
Nurturing your bees requires a keen understanding of their behavior and life cycle, giving you the power to create an environment that fosters natural foraging and contributes to a robust, healthy hive.
How to Ensure Your Hive is Thriving?
To ensure your hive thrives, you must engage in regular inspections, provide sufficient food sources, implement effective pest and disease management, and keep your environment clean and organized for your bees well-being.
These practices not only promote the health of your colony but also enhance honey production and overall hive efficiency.
1. Regular Hive Inspections
Conducting regular hive inspections is an essential part of successful beekeeping, enabling you to effectively monitor the health and productivity of your colonies. Aim to perform these inspections every 7 to 10 days during the active season to catch any potential issues early on.
During each inspection, it s vital to assess the hive conditions, such as the presence of brood, the quality and quantity of stored honey, and any signs of pests or diseases. Pay close attention to bee behavior, as a sudden drop in activity could be a clear indicator of stress or disease.
By remaining vigilant and addressing any concerns promptly, you can ensure the longevity and vitality of your hives, creating a flourishing environment for your bee populations.
2. Providing Adequate Food Sources
Providing adequate food sources, such as nectar and pollen, is essential for maintaining hive health and ensuring that your bees have the resources they need to thrive.
Bees rely heavily on a diverse array of plants to meet their food needs. When natural foraging opportunities dwindle whether due to seasonal changes, habitat destruction, or adverse weather conditions it becomes crucial for you as a beekeeper to step in.
Implementing supplemental feeding strategies, like offering sugar syrup or protein patties, can be a lifeline for sustaining bee populations.
By creating a vibrant and varied landscape that offers a wealth of food sources, you can significantly enhance their well-being and boost overall hive productivity.
By recognizing the importance of food availability, you are crucial in safeguarding these vital pollinators.
3. Proper Pest and Disease Management
Taking charge of pest and disease management is vital for your hive’s well-being, especially when controlling pests like varroa mites that can wreak havoc on bee populations.
Adopting an integrated pest management (IPM) approach a method that combines different ways to handle pests effectively is essential. This strategy combines biological, cultural, and mechanical methods to minimize the impact of these detrimental organisms.
Regular monitoring techniques, such as hive inspections and the use of sticky traps, enable you to identify pest populations early, paving the way for timely interventions.
Preventive measures, such as ensuring proper ventilation and maintaining cleanliness within the hive, play a significant role in sustaining overall hive health.
By employing techniques such as rotating hive locations and selecting resilient bee strains, you can bolster the bees’ natural defenses, creating a more sustainable and productive environment for your apiculture endeavors.
4. Maintaining a Clean and Organized Hive
Maintaining a clean and organized hive is essential for preserving the health of your bee colony and enhancing overall productivity. A tidy environment minimizes the risks associated with diseases and fosters a favorable atmosphere for your bees to thrive.
You can implement various practices, such as conducting regular inspections to identify and remove any debris, old comb, or dead bees that might harbor harmful pathogens.
Ensuring that your hive has adequate ventilation and is protected from excessive moisture will help mitigate the growth of detrimental molds.
By managing both the hive’s interior and the surrounding environment thoughtfully, including placing it away from pesticide-heavy areas, you can significantly enhance your bees’ resilience against common pests and diseases.
5. Educating Yourself on Beekeeping Best Practices
Educating yourself on beekeeping best practices is essential for the health and productivity of your hive. Continuous education through workshops, literature, and online resources empowers you to manage effectively.
By actively pursuing continuous education, you can keep yourself informed about the latest trends and techniques that lead to successful hive management.
Joining local or national beekeeping associations often gives you access to invaluable insights into bee wellness, pest control, and sustainable practices.
Exploring online seminars can also provide you with diverse perspectives and shared experiences from fellow beekeepers around the globe.
This dedication to education not only sharpens your skills but also fosters a thriving beekeeping community that collectively contributes to the well-being of these vital pollinators.
Start your beekeeping journey today by enrolling in a local workshop!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some signs that my hive is thriving?
Some signs that your hive is thriving and vibrant include an active and busy entrance, bees bringing in pollen and nectar, and a large population of bees. Regular hive inspection and monitoring for disease control are essential for maintaining these thriving conditions.
How can I tell if my hive is healthy, strong, and showing signs of wellness?
A healthy and strong hive will have a consistent brood pattern, with capped brood cells, larvae present, and hexagon structures filled with honey. The bees will also be calm and not easily agitated when you open the hive.
Monitoring bee behavior and the overall environment, including temperature and humidity, is crucial for assessing hive health.
What does it mean if my hive has a lot of honey stores and weight?
If your hive has a significant amount of honey, it indicates that the bees can find and collect enough nectar to sustain the colony. This is a sign of a thriving and productive hive with good honey production.
Efficient honey storage within the comb and frames shows optimal beekeeping practices and a balanced ecosystem.
Do I need to see the queen bee to know if my hive is thriving?
No, you do not need to see the queen bee to know if your hive is thriving. As long as you see eggs and larvae in the brood cells, it means the queen is present and laying eggs. This is a sign of a healthy and productive hive.
The consistent brood pattern and active worker bees also indicate a thriving hive.
What if my hive has many bees but no honey stores?
If your hive has many bees but no honey, the bees might struggle to find enough flowers. Act quickly! Provide supplemental feeding to help them survive.
Beekeepers should monitor the hive s weight and food sources to assess if the environment and natural resources meet the hive’s needs.
Can a hive still be thriving even if it has some dead bees outside?
Yes, it is normal for a hive to have some dead bees outside, especially during winter. As long as the dead bees are not excessive and the hive shows other signs of thriving, there is no need to worry.
Keep an eye on your hive and learn about bee behavior to keep your bees happy and healthy!