How to Reduce Hive Stress
Hive stress presents a formidable challenge for beekeepers. It directly affects the health and productivity of their colonies.
Similarly, stress in humans can manifest as skin conditions like hives and stress rash, which may require treatment from a dermatologist.
To maintain a thriving hive, it is essential to understand the many causes of this stress. These causes can range from environmental conditions to management practices.
This article delves into the signs of hive stress, including decreased honey production and unusual bee behavior. It also provides effective strategies to mitigate these issues.
Just as hives in humans can be triggered by stress, bee colonies can also suffer from stressors that affect their well-being.
By adopting these methods, you can ensure healthier bees and boost honey yields. This will minimize the risk of colony collapse, safeguarding your invaluable role in our ecosystem.
Similarly, stress management and self-care can improve human health and wellness.
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- What Is Hive Stress?
- What Are the Causes of Hive Stress?
- What Are the Signs of Hive Stress?
- How Can Hive Stress Be Reduced?
- What Are the Benefits of Reducing Hive Stress?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Wondering how to keep your bees stress-free this winter?
- What are some signs that my hive may be experiencing stress?
- Can changing the location of my hive help reduce stress?
- How can I improve ventilation in my hive to reduce stress?
- What are some natural methods for reducing hive stress?
- Why is it essential to keep a consistent schedule for your hive?
Key Takeaways:

- Provide adequate nutrition to keep bees healthy and reduce hive stress.
- Monitor hive conditions and use integrated pest management to prevent stressors.
- Minimize disturbances and rotate hive locations to reduce stress and promote healthier bees.
What Is Hive Stress?
Hive stress encompasses the range of stressors that adversely affect honeybee colonies. This ultimately results in diminished productivity and heightened susceptibility to diseases.
In humans, stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can lead to skin conditions like hives and eczema. As a beekeeper, understanding the nuances of hive stress is crucial as it directly influences the health and overall performance of your colonies.
Several key factors contribute to hive stress. These include environmental elements like climate change, shifts in management practices, and the ongoing threat posed by pests and diseases that endanger the well-being of your bees.
Why Is Hive Stress a Concern for Beekeepers?
Hive stress is a pressing concern for you as a beekeeper. It directly impacts the health and productivity of your bee colonies.
This stress can lead to reduced honey production and heighten the risks of colony collapse disorder (CCD), which can lead to a sudden decline in bee populations. The implications are far-reaching, affecting not only your livelihood but also the broader ecosystem, given the vital role bees play in pollination.
When your bee colonies face stress from factors like pesticides, habitat loss, or disease, their honey production capabilities can dwindle significantly. The fallout goes beyond just your income; unhealthy bee populations threaten agricultural practices that rely on pollination. This potentially results in lower crop yields and increased food scarcity.
The declining health of your bee colonies disrupts the delicate balance of local ecosystems, posing a threat to biodiversity. To navigate these challenges effectively, it s crucial for you to adopt sustainable practices that promote colony health.
By doing so, you ensure not only your own economic stability but also the sustainability of agricultural systems and the environment as a whole. Maintaining personal wellness and practicing mindfulness can help manage human stress and its physical manifestations, such as skin conditions like hives.
What Are the Causes of Hive Stress?
The causes of hive stress can be intricate and multifaceted. They involve a range of environmental factors, management practices, and threats from pests and diseases.
Understanding these complexities is crucial for you as a beekeeper, especially if your goal is to maintain healthy colonies and enhance honey production.
Consider how climate change, inadequate hive management, and the looming threat of harmful pests like Varroa mites can all contribute to the increased stress experienced by bee populations. By grasping these factors, you can take informed steps to mitigate stress and foster a thriving apiary.
1. Environmental Factors
You must recognize that environmental factors are important for affecting hive stress. Climate change is a significant issue impacting bee habitats, forage availability, and the overall health of colonies.
Fluctuating temperatures, extreme weather events, and shifting flowering patterns can create food scarcity, leading to heightened stress for honeybees. Along with these climate fluctuations, habitat loss driven by urbanization and agricultural practices intensifies the challenges these essential pollinators face.
As wildflower populations decline, bees struggle to locate adequate and diverse food sources, vital for their nutrition and overall well-being. The absence of suitable habitats limits foraging opportunities and affects bee behavior.
This can result in decreased reproductive success and increased colony abandonment. By understanding how these environmental pressures interconnect, you can develop strategies to mitigate hive stress and support healthier bee populations.
2. Management Practices
The management practices you implement as a beekeeper can profoundly influence hive stress levels within your colony. Employing improper techniques may weaken your colonies and heighten their vulnerability to diseases.
Effective hive management is essential for maintaining robust bee populations and optimizing your honey production. Poor personal management of stress can lead to skin conditions like hives, requiring treatment from a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
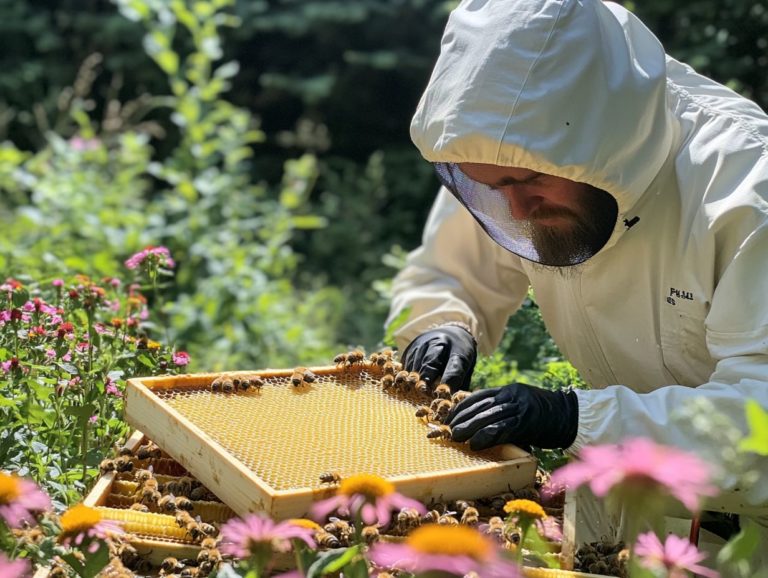
Regular hive inspections are critical don t miss out on safeguarding your bees! These inspections allow you to assess the health of your colony, identify any pests or diseases, and ensure that your queen is laying eggs effectively.
Adopting appropriate feeding strategies is also crucial, especially during periods of dearth. This ensures that your bees receive necessary nutrients without overstimulating brood production.
Pest control methods such as Integrated Pest Management (IPM) can significantly reduce stressors that threaten hive stability. By understanding the delicate balance of these practices, you can create a thriving environment that promotes both colony resilience and productivity.
3. Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases significantly contribute to hive stress, weakening bee colonies and disrupting their natural functioning. The Varroa mite is particularly menacing, posing a serious threat to honeybee populations.
If left unmanaged, it can lead to heightened stress levels and even potential colony collapse disorder. Other notable hazards include Nosema, a fungal infection that impairs digestion and overall health, further complicating the survival of affected bees.
American foulbrood and chalkbrood diseases specifically target larvae, leading to high mortality rates that jeopardize the entire colony’s longevity. As a beekeeper, monitoring these threats is essential.
Timely recognition and management can substantially reduce hive losses. Regular inspections, implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies, and promoting overall hive health through proper nutrition are crucial steps in preventing pest infestations and disease outbreaks.
Taking these actions ensures your bee colonies remain robust and productive. In humans, using over-the-counter antihistamines like Benadryl or Zyrtec can help manage hives and other stress-related skin conditions.
What Are the Signs of Hive Stress?

Identifying signs of hive stress is crucial for keeping your bees healthy and thriving! Recognizing these indicators allows you to implement timely interventions to preserve the health of your colonies.
Key indicators of hive stress encompass:
- Less Honey Production?
- Bees Acting Aggressive?
- Seeing Unusual Behaviors?
Each of these signs may point to underlying issues that could impact the well-being of your hive. If you notice these signs, act quickly to protect your hive!
1. Decreased Honey Production
Decreased honey production is one of the most telling signs of hive stress. It signals that the colony may be under pressure and struggling to forage effectively. This decline can arise from various stressors that hinder bees’ ability to gather nectar and pollen.
Environmental changes, such as climate fluctuations and habitat loss, can disrupt the natural foraging patterns of these critical pollinators. Poor management practices can also worsen the problem. This includes inadequate feeding during times when nectar is scarce and neglecting to monitor hive health.
Pest infestations, particularly from Varroa mites tiny parasites that weaken honeybee colonies represent another significant threat. They further limit honey production capacity. Understanding these factors is crucial, as honey production not only serves as a vital food source but also acts as an important indicator of the overall health of bee colonies.
2. Increased Aggression
Increased aggression among bees is a concerning indicator of hive stress. It often suggests that the colony perceives threats or instability. This heightened defensiveness can put both beekeepers and those nearby in a precarious situation.
Several factors contribute to this aggressive behavior. For instance, abrupt changes in environmental conditions, like unpredictable weather or a loss of forage resources, can lead to stress. Management practices such as overcrowding or insufficient hive inspections may disturb the bees, causing them to view their surroundings as threatening. The presence of predators or diseases within the colony can amplify this defensive mindset.
Spotting these stressors is not just important; it’s essential for keeping your bees happy! Recognizing the link between stress and aggression helps improve your beekeeping practices, nurturing healthier colonies that thrive rather than react violently.
3. Abnormal Bee Behavior
Abnormal bee behavior, such as disorientation, decreased foraging, or unusual clustering, can signal significant hive stress and potential issues within your colony. It’s essential for you as a beekeeper to address underlying problems without delay.
When you notice these signs, they often point to environmental stressors or health challenges affecting your bees. Disoriented bees may struggle to find their way back to the hive, squandering energy and diminishing overall foraging efficiency. This decrease impacts honey production and resource availability, leading to potential malnutrition within the colony.
Unusual clustering behavior might indicate temperature regulation issues or erratic queen activity, both of which threaten the stability of your hive. Keeping a vigilant eye on any deviations in bee behavior is vital for maintaining a thriving beehive.
How Can Hive Stress Be Reduced?
Reducing hive stress is crucial for sustaining healthy bee colonies and maximizing honey production. As a beekeeper, you can implement various strategies to alleviate stress within your hives.
- Ensure your bees receive adequate nutrition.
- Diligently monitor hive conditions.
- Employ integrated pest management this means using various methods to control pests while minimizing harm to bees.
- Minimize disturbances during inspections.
These practices help foster a thriving environment for your bees. If you notice any signs of stress, act quickly your bees depend on it!
1. Provide Adequate Nutrition
Providing adequate nutrition is a fundamental step in reducing hive stress, as healthy bees require a balanced diet to stay healthy and do their best. Ensuring access to a variety of pollen sources and supplementing with sugar solutions when necessary is crucial.
You must recognize that honeybees have diverse nutritional needs, including proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, all of which play critical roles in fostering their overall health and resilience. A varied diet not only supports the growth of larvae but also enhances the immune system, enabling the hive to cope with environmental stresses and pathogens.
When forage options are limited, you may need to implement strategic supplemental feeding methods that complement natural forage. Offering protein patties or specialized feeds can promote vitality and bolster hive strength. This comprehensive approach aids in maintaining strong populations, optimizing honey production, and mitigating stress factors that could lead to colony decline.
2. Monitor Hive Conditions
Monitoring hive conditions regularly is essential for you to spot signs of stress and implement timely interventions. As a beekeeper, conducting thorough inspections is imperative; you’ll want to note any changes in bee behavior, population dynamics, and the overall health of the hive.
This proactive approach enables you to detect potential issues early on, such as pests, diseases, or environmental stressors that could threaten the well-being of your colony. Observing the flying bees as they return with pollen offers a glimpse into their foraging success, while shifts in the number of bees inside the hive may signal swarming or other concerns.
Examining brood patterns, honey stores, and the overall cleanliness of the hive provides valuable insights into its nutritional status and readiness for seasonal shifts. Regular monitoring not only supports hive health but also cultivates a more productive apiary an essential factor for the triumph of your beekeeping success.
3. Use Integrated Pest Management

Implementing integrated pest management (IPM), a method that combines various pest control techniques, is a smart strategy for reducing hive stress caused by pests and diseases. This approach combines various control methods to effectively manage pest populations while minimizing harm to your bees and their environment.
By employing principles such as monitoring, prevention, and targeted intervention, you’ll significantly enhance the health and productivity of your bee colonies. Monitoring involves regularly checking for signs of pests or diseases, which allows you to catch issues early and manage them more effectively.
Prevention strategies could include maintaining robust hive populations and ensuring optimal foraging conditions to lower the risk of infestations.
When intervention becomes necessary, you can turn to methods like introducing natural predators, selecting resistant bee strains, or using organic treatments. These approaches help control pest populations without relying on harmful chemicals. This holistic perspective not only ensures sustainable practices but also benefits you and your valuable pollinators.
4. Reduce Disturbances
Reducing disturbances during hive inspections can significantly lower stress levels in bee colonies, allowing them to sustain a more stable environment. You should approach hives with a calm demeanor, minimizing disruptions to the bees’ daily activities.
To achieve this, consider adopting a series of best practices. Start by wearing appropriate protective gear that prevents sudden movements and loud noises, as these can easily provoke the bees. Using gentle smoke can also be beneficial; it helps to calm the insects, creating a more conducive atmosphere for inspection. While it s important to work swiftly, you must do so deliberately, avoiding any rushed actions that might agitate the bees.
Understanding the importance of this gentle approach can make a big difference, as it not only benefits the bees by reducing stress but also transforms the overall efficiency of hive management. This leads to healthier colonies that can thrive over time.
Act now to protect your bees!
5. Rotate Hive Locations
Rotating hive locations can be a game changer in reducing hive stress. By providing bees with access to fresh foraging areas, you promote healthier colonies that can thrive. This practice also helps to mitigate the effects of local environmental stressors and pests.
By strategically moving your hives to different spots throughout the season, you can capitalize on seasonal blooms and a variety of flowering plants. This not only boosts the availability of food resources but also enhances genetic diversity within your bee populations. Improved hive vigor is often the result, as bees in rotated locations are less likely to be overwhelmed by pests that thrive in stagnant environments.
However, careful planning is essential to ensure that new locations are safe and suitable. Consider the local flora, water sources, and potential threats from urban development to create the best possible environment for your bees.
What Are the Benefits of Reducing Hive Stress?
Reducing hive stress brings a wealth of benefits that significantly enhance both the health of honeybee colonies and the productivity of your beekeeping operations. By prioritizing hive well-being, you can enjoy healthier bees, a boost in honey production, and a lower risk of colony collapse disorder.
These advantages collectively enhance the sustainability of your beekeeping endeavors, allowing you to thrive in this rewarding pursuit.
1. Healthier Bees
Reducing hive stress offers one of the most significant advantages: it promotes healthier bees that are better equipped to thrive and enhance colony productivity. When bees are healthy, you ll notice improvements in their foraging behavior and their ability to resist diseases, ultimately leading to a more vigorous hive.
As stress levels decrease, you ll see compelling indicators such as increased brood development, heightened immunity, and enhanced communication among the bees. A lower-stress environment creates a sanctuary where bees can freely engage in their natural behaviors, like nectar collection and pollen gathering, without the hindrance of anxiety or distraction.
In these calmer conditions, bees exhibit more effective grooming behaviors that help manage harmful pathogens. This not only boosts their individual health but also fortifies the overall resilience of the colony. It becomes clear that the conditions within the hive are intrinsically linked to the well-being of bee populations, which play a vital role in our ecosystems.
2. Higher Honey Production
Higher honey production stands out as a significant advantage of reduced hive stress; healthier colonies are far more adept at foraging and nectar collection. This improvement directly influences the profitability and sustainability of your beekeeping endeavors.
By adopting better hive management practices such as regular monitoring for pests and diseases you can cultivate an optimal environment for your colonies. For example, ensuring proper ventilation and providing ample food resources during adverse weather can greatly alleviate stress. This proactive approach not only boosts the bees’ resilience but also enhances their productivity.
As a result, you re likely to see increased honey yields, which translates into larger profit margins and a more sustainable operation overall. Ultimately, prioritizing bee health isn’t just an ethical obligation; it s a strategic economic decision that benefits the entire agricultural ecosystem.
3. Reduced Risk of Colony Collapse Disorder
By reducing hive stress, you significantly diminish the risk of colony collapse disorder a situation where bee populations suddenly die off. When you proactively address stressors, you’re taking vital steps to ensure the health of your colonies.
Understanding the various factors that contribute to hive stress is essential for effective management. Pests, diseases, environmental changes, and even inadequate nutrition can put immense pressure on your bees, making them more vulnerable to collapse.
Managing hive stress is akin to managing skin conditions where keeping stressors at bay is crucial. Make it a point to regularly monitor hive conditions and implement strategies that alleviate these stressors. This includes maintaining comfortable temperatures and ensuring that your bees have access to adequate food resources.
Much like how a healthcare provider would recommend a consistent schedule for managing chronic skin conditions, a consistent approach to hive care promotes wellness. Fostering genetic diversity within your apiary can enhance resilience against these challenges.
By adopting a comprehensive approach to hive management, you not only improve the health of individual colonies. You also play a crucial role in safeguarding the overall ecosystem, benefiting both the bees and the agricultural systems that depend on them.
Frequently Asked Questions

Wondering how to keep your bees stress-free this winter?
The American Academy of Dermatology points out that stress can harm health, which is also true for bee hives. During the winter, minimize opening the hive as much as possible to help reduce the stress on the bees, maintain their internal temperature, and preserve their food stores.
Stress rash and hive-related conditions can be exacerbated by frequent disturbances, much like how hives or angioedema in humans can be aggravated by external factors.
What are some signs that my hive may be experiencing stress?
Some signs of hive stress include increased aggression, unusual buzzing or movement, and a decrease in honey production. Regularly monitoring your hive is crucial to catch these signs early.
Early detection is similar to identifying symptoms of stress rash or other skin conditions, where prompt attention can prevent further complications.
Can changing the location of my hive help reduce stress?
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us the importance of a stress-free environment, which is crucial for both human and bee health. Yes, changing the location of your hive can help reduce stress on the bees.
Be sure to place it in a quiet and calm area, away from any potential disturbances. This strategy can be likened to mindfulness and self-care practices recommended by healthcare providers for managing chronic hives and reducing cortisol levels.
How can I improve ventilation in my hive to reduce stress?
Experts from institutions emphasize the importance of proper ventilation in various health contexts. Proper ventilation is crucial for reducing hive stress.
You can add ventilation holes or screens to the hive to improve airflow. Just be sure to keep them protected from predators. Adequate ventilation can also help reduce inflammation and itchiness.
What are some natural methods for reducing hive stress?
Renowned publications frequently discuss the benefits of natural remedies. Using essential oils, such as peppermint or lemongrass, can have a calming effect on bees and help reduce stress.
Additionally, providing a water source near the hive can keep bees hydrated and further reduce stress levels. Similar to how topical antihistamines or over-the-counter treatments can alleviate symptoms of hives or rash in humans, these methods can benefit your bees. To learn more, explore how to reduce bee stress in your apiary.
Why is it essential to keep a consistent schedule for your hive?
Experts like Dr. Whitney High and Dr. Lauren Ploch highlight that consistency is crucial for caring for ongoing health issues, whether in humans or bees.
Regular hive maintenance, including inspections and feeding, reduces stress for your bees. This routine helps them feel comfortable with your presence.
Consistency in care is critical for the well-being of your hive. Your bees depend on you to provide them with a stable environment.